In my data structures and algorithms course, I had a topic which gave me a general overview on how hashing helps to store and retrieve data efficiently. Some of the concepts fascinated me and I decided to implement them for recreation.
Some basic terms that I’ll be using in my explanation are:
| Terms | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Key | An input. |
| Hashing | The process of taking an input key and generating a parameter which is used to store the key. |
| Hash Function | A function that is responsible for taking the key as input, processing it and providing an output that is used to store the key. |
| Bucket | A place where the key is stored. |
| Hash table | A table which stores all of the buckets. |
| Bucket index | An index or a reference to where the key is stored; or simply put, the address of the bucket in the hash table. |
| Collision | When one or more keys (input) produce the same bucket index (output), a collision is said to occur. |
| Overflow | When a hash table has reached the limit of how many keys it can store, adding any more elements will cause an overflow to occur. |
To resolve a collision, we use different collision resolution techniques. Three of them are:
Chaining
Important points to note
- This type of technique uses linked lists to store keys.
- When a collision occurs, one can simply add the incoming key to the linked list.
- This solution is able to dynamically store incoming keys without requiring us to manually resizing it.
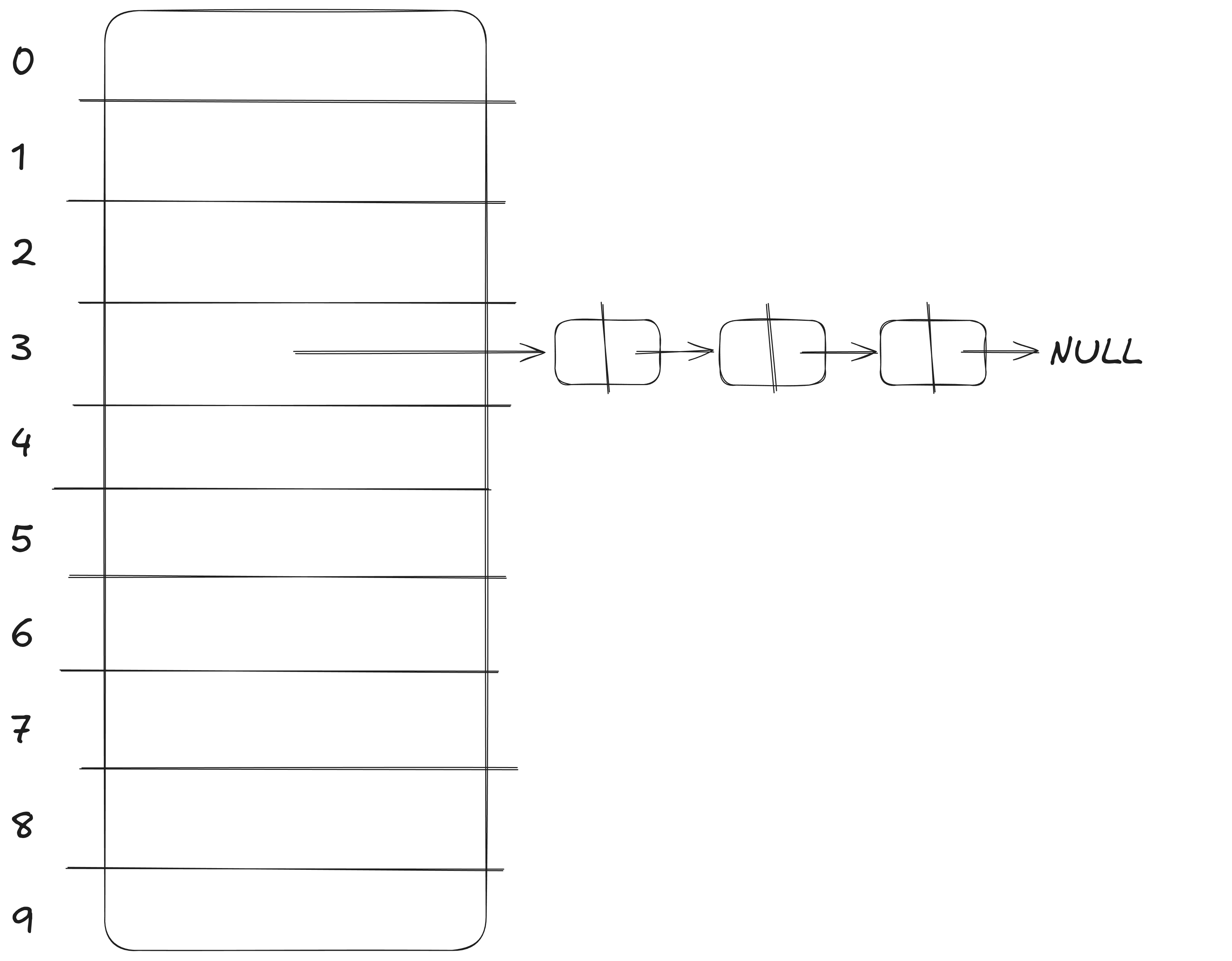
- Each index of the hash table points to the head of the linked list that stores the most recent element of the bucket.
- Each element that is in the linked list points to the next element. If the current element is the last element, it will point to null.
Visual representation
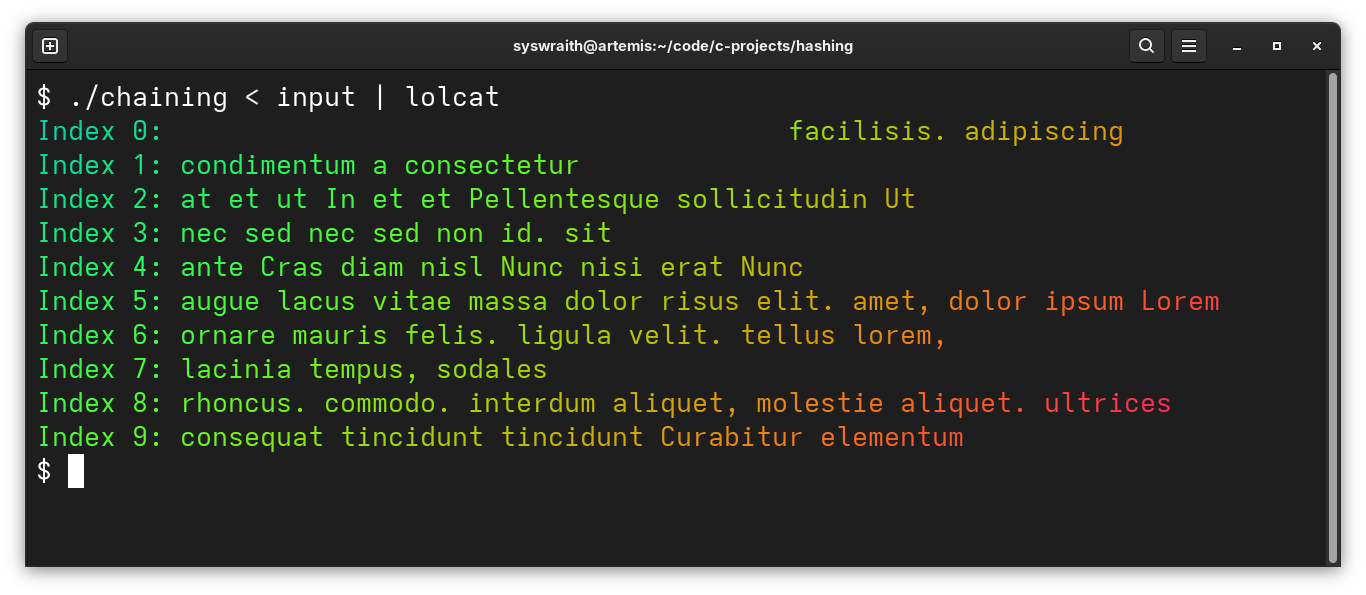
C code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_INDEX 10
typedef struct bucket_t {
char *data;
struct bucket_t *next;
} bucket;
typedef struct bucket_index_t {
bucket *index_ptr;
} bucket_index;
bucket_index table[MAX_INDEX];
void initialize_table() {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_INDEX; i++)
table[i].index_ptr = NULL;
}
void push_key(char *word) {
char *key = malloc(strlen(word) + 1);
strcpy(key, word);
int key_length = strlen(key);
int hash_value = key_length % MAX_INDEX;
bucket *new_entry = malloc(sizeof(bucket));
new_entry->data = key;
new_entry->next = NULL;
if (table[hash_value].index_ptr == NULL) {
table[hash_value].index_ptr = new_entry;
} else {
bucket *tmp = table[hash_value].index_ptr;
new_entry->next = tmp;
table[hash_value].index_ptr = new_entry;
}
}
void print_hash_table() {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_INDEX; i++) {
printf("Index %d: ", i);
bucket *head = table[i].index_ptr;
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%s ", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void delete_hash_table() {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_INDEX; i++) {
bucket *head = table[i].index_ptr;
while (head != NULL) {
bucket *tmp = head->next;
free(head->data);
free(head);
head = tmp;
}
table[i].index_ptr = NULL;
}
}
int main() {
int limit = 100;
initialize_table();
while (limit--) {
char buff[100] = {0};
scanf("%99s", buff);
push_key(buff);
}
print_hash_table();
delete_hash_table();
return 0;
}Output
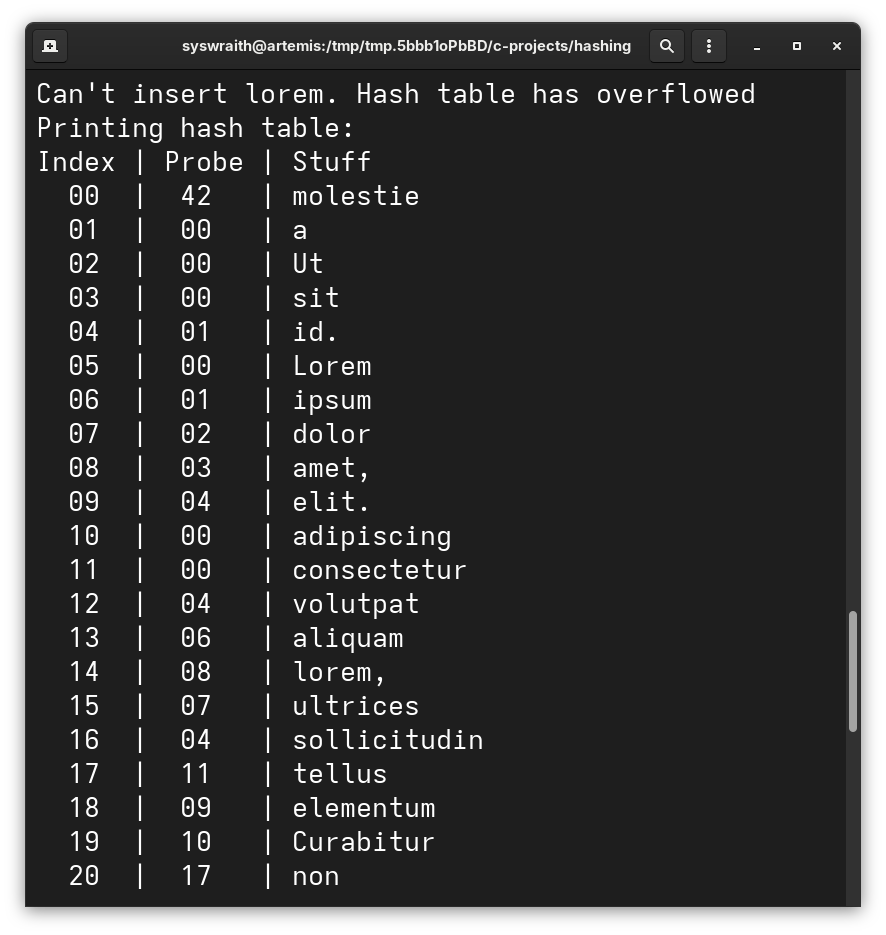
 Since the hash function is
Since the hash function is k % 10, the index for 0 and 10 are the same, thus the leading spaces.
Linear Probing and Quadratic probing
- Both Linear and Quadratic probing use a simple index table structure.
- The hash table may be defined as a simple array that can hold the value and the probe number.
- The probe number is the number of tries/probes taken to search for an empty bucket.
- Since the table size is fixed, an overflow can occur.
Difference between linear and quadratic probing
- S = Table size
- N = Probe number
- x = Key value
| Differences | Linear Probing | Quadratic Probing |
|---|---|---|
| Hash function used | (hash(x) + N) % S | (hash(x) + N*N) % S |
| Primary clustering | Occurs | Does not occur |
| Secondary clustering | Occurs | Occurs |
| Search time | Drastically increases | Increases gradually |
C code
1. Linear Probing
#include <float.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#define MAX 50
typedef struct bucket_t {
char *data;
int probe;
} bucket;
bucket *table[MAX];
void init_table();
int calc_index(char *word);
int probe(int bucket_index);
void create_element(char *key);
void delete_table();
void print_table();
void init_table() {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
table[i] = NULL;
}
int probe(int bucket_index) {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
int circular_value = (bucket_index + i) % MAX;
if (table[circular_value] == NULL) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int calc_index(char *key) {
int index = strlen(key) % MAX;
return index;
}
void create_element(char *word) {
char *key = malloc(strlen(word) + 1);
strcpy(key, word);
int bucket_index = calc_index(key);
int probe_value = probe(bucket_index);
if (probe_value == -1) {
printf("Can't insert %s. Hash table has overflowed\n", key);
free(key);
return;
}
int circular_value = (bucket_index + probe_value) % MAX;
bucket *element = malloc(sizeof(bucket));
element->data = key;
element->probe = probe_value;
printf("Inserting %s at index %d\n", key, circular_value);
table[circular_value] = element;
}
void delete_table() {
printf("Deleting table\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
if (table[i] == NULL)
continue;
free(table[i]->data);
free(table[i]);
table[i] = NULL;
}
}
void print_table() {
bool table_empty = true;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
if (table[i] != NULL) {
table_empty = false;
break;
}
}
if (table_empty) {
printf("Nothing to print. Table is empty\n");
return;
}
printf("Printing hash table:\n");
printf("Index | Probe | Stuff\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
if (table[i] != NULL)
printf(" %.2d | %.2d | %s\n", i, table[i]->probe, table[i]->data);
}
int main(void) {
init_table();
int limit = 100;
while (limit--) {
char buff[100] = {0};
scanf("%99s", buff);
create_element(buff);
}
print_table();
delete_table();
print_table();
return 0;
}2. Quadratic Probing
#include <float.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#define MAX 50
typedef struct bucket_t {
char *data;
int probe;
} bucket;
bucket *table[MAX];
void init_table();
int calc_index(char *word);
int probe(int bucket_index);
void create_element(char *key);
void delete_table();
void print_table();
void init_table() {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
table[i] = NULL;
}
int probe(int bucket_index) {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
int circular_value = (bucket_index + (i*i)) % MAX;
if (table[circular_value] == NULL) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int calc_index(char *key) {
int index = strlen(key) % MAX;
return index;
}
void create_element(char *word) {
char *key = malloc(strlen(word) + 1);
strcpy(key, word);
int bucket_index = calc_index(key);
int probe_value = probe(bucket_index);
if (probe_value == -1) {
printf("Can't insert %s. Hash table has overflowed\n", key);
free(key);
return;
}
int circular_value = (bucket_index + (probe_value*probe_value)) % MAX;
bucket *element = malloc(sizeof(bucket));
element->data = key;
element->probe = probe_value;
printf("Inserting %s at index %d\n", key, circular_value);
table[circular_value] = element;
}
void delete_table() {
printf("Deleting table\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
if (table[i] == NULL)
continue;
free(table[i]->data);
free(table[i]);
table[i] = NULL;
}
}
void print_table() {
bool table_empty = true;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
if (table[i] != NULL) {
table_empty = false;
break;
}
}
if (table_empty) {
printf("Nothing to print. Table is empty\n");
return;
}
printf("Printing hash table:\n");
printf("Index | Probe | Stuff\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
if (table[i] != NULL)
printf(" %.2d | %.2d | %s\n", i, table[i]->probe, table[i]->data);
}
int main(void) {
init_table();
int limit = 100;
while (limit--) {
char buff[100] = {0};
scanf("%99s", buff);
create_element(buff);
}
print_table();
delete_table();
print_table();
return 0;
}Output